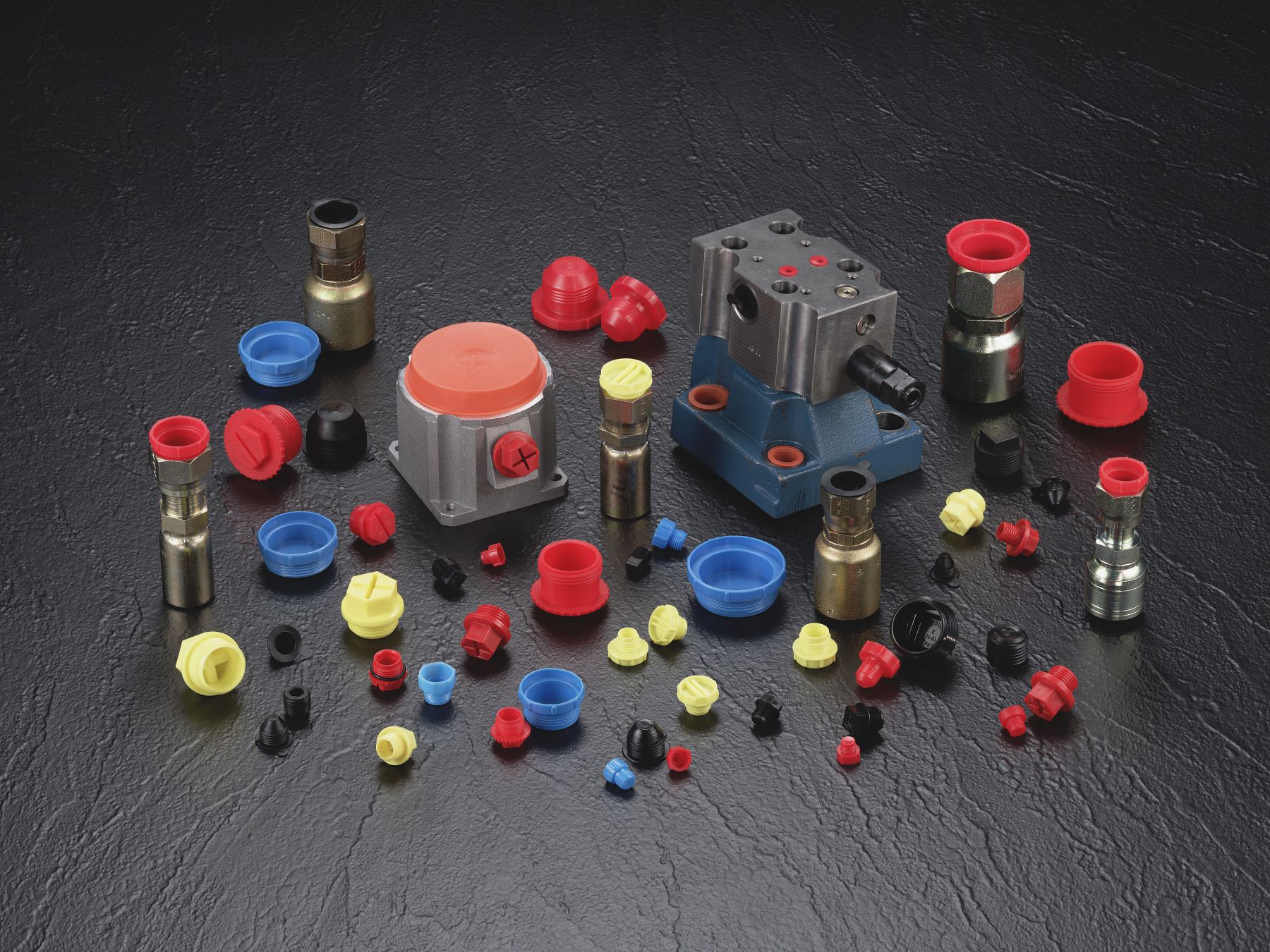

Threaded parts require protection during finishing, shipping, storage and operations. Depending on your component and where its threads are located a protective cap or plug can be the ideal protection solution.
Learn more about benefits and common uses, as well as different types of threads in this convenient thread protection guide.
Placing whatever you can find on the shop floor over threads when performing finishing operations may get the job done, but these types of imprecise solutions can leave parts open to damage. Beyond this, you’ll continually be looking for a new “masking” solution when the stop-gap wears down or completely fails.
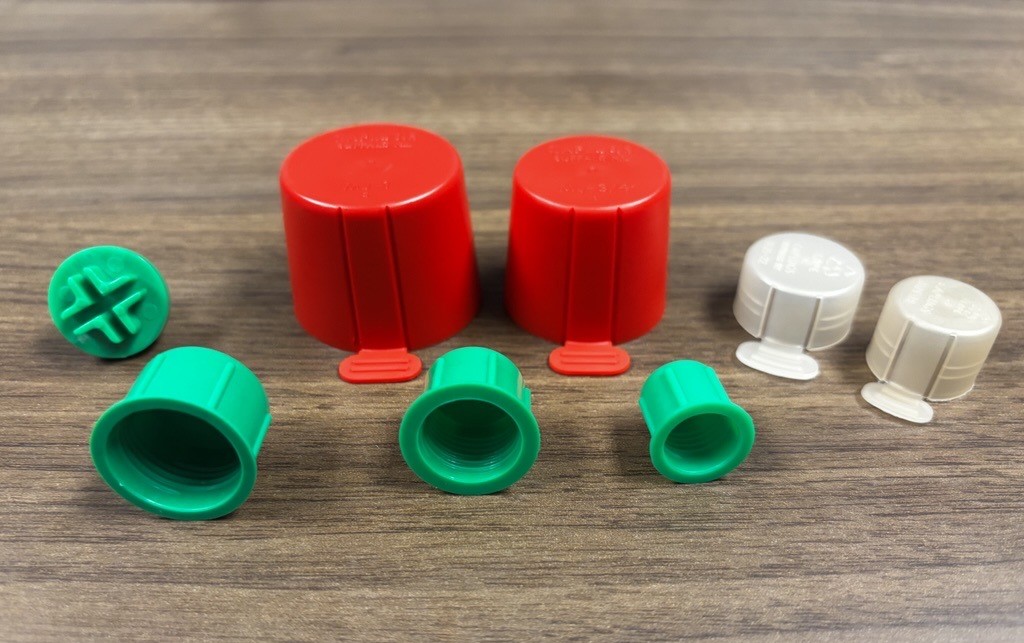
A threaded cap or plug can mask off both inner and outer threads and provides a snug fit during the entire finishing process. These parts are typically used for finishing that doesn’t involve high heat, such as wet painting, but options are available to offer resistance in higher temperature operations.

Threaded Cap for Shipping
It’s no secret that packages and their contents slide and bang around when shipped. Protect against rough shipping conditions and improper handling of packages with the placement of a threaded cap or plug.
Adding these onto the end of your pipes, fittings and other threaded parts before delivery can prevent a variety of issues during the shipping process including galling, burrs, scratches, mashed threads and more.
While your parts may be able to stand up to harsh weather and rugged operations, FOD (Foreign Object Debris/Damage) is a danger that even the toughest components can fall prey to.
A threaded cap or plug works well at preventing FOD from entering and damaging a finished product and protects against damaged threading as well as unwanted impedances associated with FOD.
Whether out in the field working on oil and gas lines, maintaining hydraulic equipment or working on an engine, chassis or transmission components for a car or plane, having a proper protective cap or plug on threaded parts keeps them secure until they will be used.
These can easily be taken on and off as needed, and don’t need to be replaced regularly, keeping your operations and budget on track.
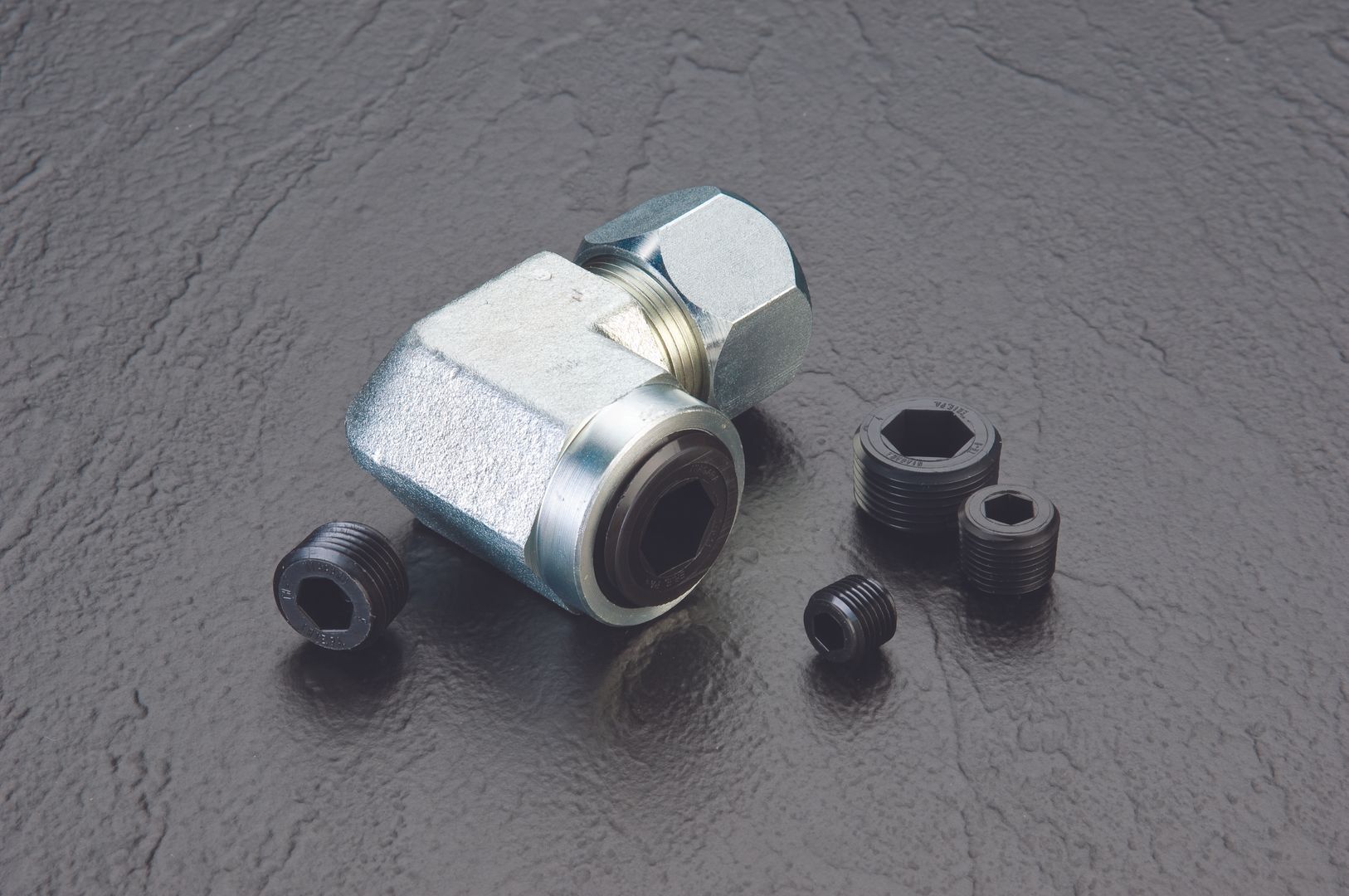

Internal NPT Threads Protected with NPT Plug
National Pipe Thread (NPT) is the U.S. standard pipe thread, measured in threads per inch with a 60° thread angle. NPTs distinguish themselves by being tapered, with a tapered angle of 1°47' (1.7833°), and are usually found on pipes and hydraulic fittings. The taper design makes for a tight seal when closed off.
Protective caps and plugs are available for NPT threads in threaded and non-threaded based on need. An NPT cap or NPT plug can protect thread sizes ranging from 1/16" NPT to 4" NPT. These threads and their protectors are often found in aerospace and military aviation applications, with an ability to stand up to high vibrations.
Unified threads are commonly used in the U.S. and Canada and are also measured in threads per inch with a 60° thread angle. A unified thread differs from an NPT by having a straight thread that distributes load and stress more evenly.
The two most common types of unified threads are unified fine (UNF) and unified coarse (UNC). UNF has a finer pitch while UNC has a wider pitch. With its finer pitch, UNF creates a tighter seal.
Other commonplace unified threads are unified extra fine (UNEF), which have an even finer pitch than UNF, and unified special (UNS), that are used when a standard series doesn’t meet requirements.
An example designation is a 1-8 UNC. This is a 1" thread with eight threads per inch. A 1-12 UNF is a 1" thread with 12 threads per inch. A 1-20 UNEF is a 1" thread with 20 threads per inch. It’s important to note that threads per inch will differ for each based on the diameter. Unified thread caps and unified thread plugs are available to be used in a variety of applications including hydraulic, aerospace, automotive and aviation.
Metric Thread Protection
Metric threads are the worldwide standard outside of the U.S., with its pitch being measured in millimeters between a thread.
Metric threads are categorized with an "M" followed by the diameter in millimeters and the pitch. A M12 x 1.5 metric thread, for example, has a diameter of 12 mm and a pitch of 1.5 mm. Like unified threads, metric threads have a straight thread and have a thread angle of 60°. Common metric threads include metric fine and metric coarse.
Metric threads and their protective caps and plugs are most often used in aviation, automotive, hydraulics and electronics industries.
British Standard Pipe (BSP) threads are commonly seen on pipes and plumbing connections in the U.K. They differ from their metric counterparts by being measured in threads per inch, have a 55° thread angle and use the Whitworth thread form (rounded at the crest and root).
BSPs are unique in that they have both straight and tapered options. This is helpful for those who regularly require different seals for different applications. The tapered thread will provide a tighter, more secure fit while the straight thread is better for fittings that are regularly installed and removed.
BSP threads and their threaded plugs and caps are ideal for low-pressure plumbing and piping systems.
Universal Pull Plug
SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers) straight threads are used in automotive and hydraulic applications to provide a leak-free seal. Male SAE connectors typically have an O-Ring Boss to create a tight seal with a SAE female connector.
The designation for SAE threads is a number (e.g., -8) that corresponds to the thread size in sixteenths of an inch. In this example, the -8 thread size means the diameter is 8/16 or 1/2 inch.
Universal threads are another commonly used thread as they are compatible with most of the threads listed above, being able to connect to NPT, UNF, metric and BSP threads. Universal thread plugs can seal 1/8 NPT, 7/16 UNF, 1/8 BSP and M10 threads.
Threaded cap and plug protection is available for universal and SAE threads as well as for screw caps and other threaded protectors.
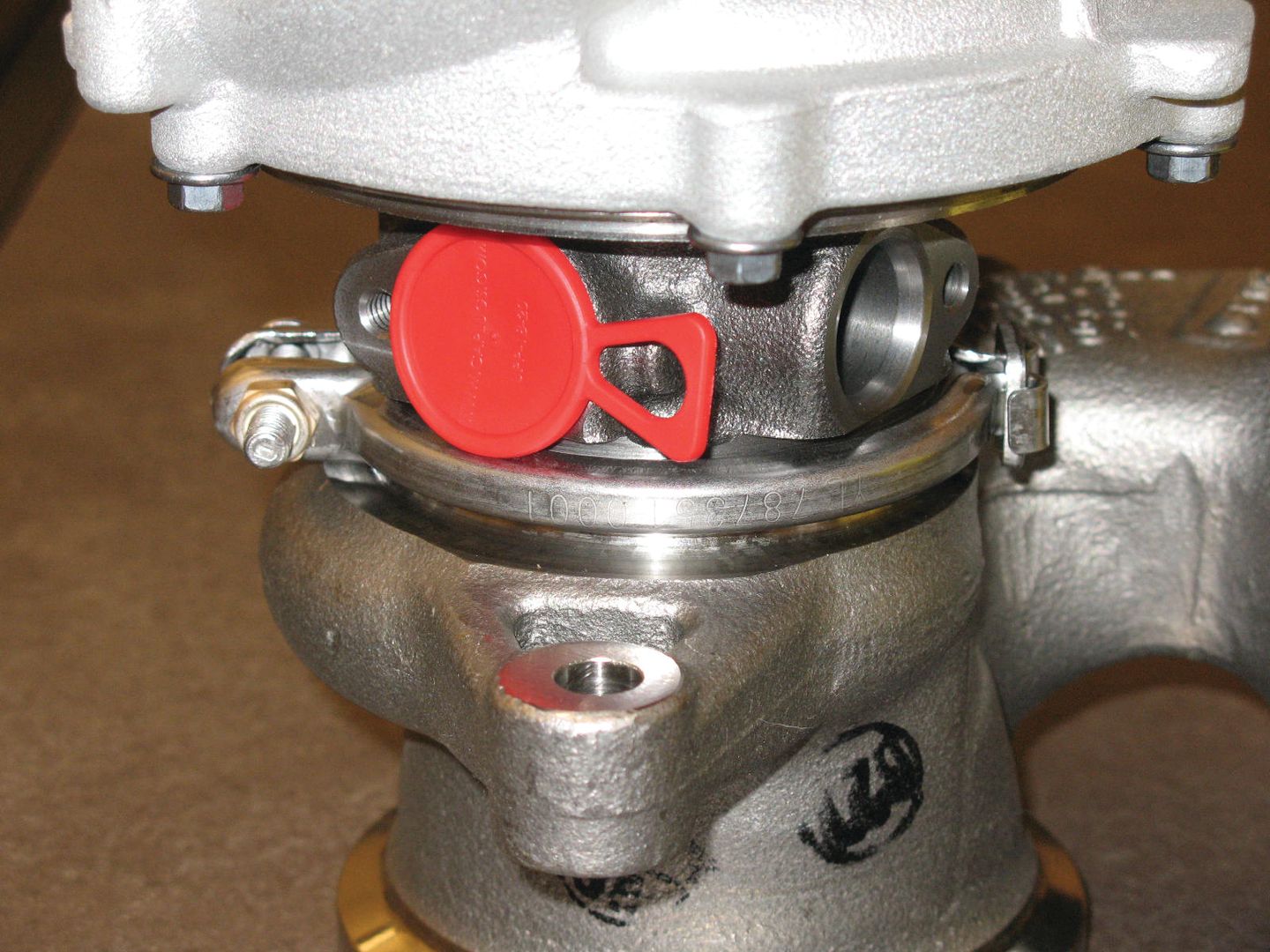
Hydraulic equipment is typically used in rugged, outdoor settings, meaning threaded fittings and connectors need to be in near perfect condition when in use in mining, agriculture, construction and industrial operations.
To protect these components, threaded caps and plugs are often used to not only protect delicate threads, but also to prevent FOD damage. The avoidance of such damage can ensure threaded connections remain secure throughout operations and that fluids aren’t exposed to the environment and workers.

Threaded Aluminum Plugs
Anyone who has seen an aircraft or spacecraft assembled understands the number of threaded parts and fittings that need to be sealed off during assembly and finishing.
Caps and plugs play a vital role in preventing damage to threads, ensuring they remain undamaged through assembly and operation.
Additionally, threaded caps and plugs do a great job of preventing external impacts from FOD and are important during anodizing and plating processes, allowing finishing to be confined to the right area.
Threaded aluminum caps and plugs are often used to protect these fittings with many meeting National Aerospace Standards (NAS).
Each vehicle that runs through an assembly line has thousands of parts. Many of these parts are threaded and will eventually be fastened with nuts, bolts and screws for the proper functioning and safety of the vehicle. Before this can happen, there are several steps where threads will need to be protected.
From finishing to shipment, storage and other key processes, threaded caps and plugs play a pivotal role in keeping unwanted materials out of fuel, transmission, steering and suspension systems that can cause major headaches or critical failures if not properly sealed.
Oil and gas operations cannot afford poor drilling performance. To avoid issues, many oil and gas companies go to great lengths to protect drill bits and their threads during finishing, shipment and storage.
Oilfield and gas pipes also need to be protected during shipment and storage. Threaded caps and plugs can keep these threads in like-new condition and can help prevent leaks in certain settings.
With so many threads and threaded protection options on the market, you may have questions about what the right options are for your applications. Reach out to our experienced team directly at your convenience or browse our threaded parts to learn more.